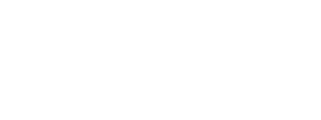Category: Publications
Search News
Categories
Archives
New approach offers hope for people with rare eye cancer
21st January 2026
A more active approach to monitoring and treating people with a rare eye cancer (known as uveal melanoma) that has spread to the liver could help some patients to live longer, according to researchers at Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London. The findings, from a retrospective study of the largest UK cohort of patients with this condition to date, offer an encouraging sign of progress in this rare and difficult-to-treat cancer.
Read moreDiscovery reveals new understanding of cancer-driving proteins in rare brain tumours and beyond
7th November 2025
Scientists have discovered that a single letter change in a gene called PRKCA drives a rare and hard-to-treat brain cancer, chordoid glioma, through an entirely unexpected mechanism. The findings could open up new ways to design targeted treatments for this difficult-to-treat disease, and possibly for other cancers involving the same gene.
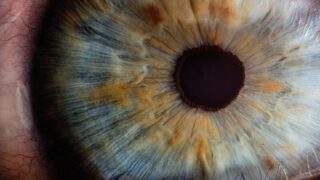
Read moreBlood test helps guide immunotherapy for bladder cancer
22nd October 2025
A new clinical trial led by Professor Thomas Powles at Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London, has shown that a blood test to detect tumour DNA could help doctors decide which patients with bladder cancer are most likely to benefit from further treatment after surgery. The new approach improved survival in those identified as high-risk while safely sparing low-risk patients from unnecessary side effects.
Read moreNew AI model sheds light on high-risk skin cancer: Q&A with the authors
30th September 2025
Researchers have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) tool that could help doctors identify which skin cancers are most likely to spread. We spoke to Professor Jun (Alex) Wang, a group leader at BCI, and Dr Emilia Peleva, a Clinical Research Fellow and dermatologist in his team, about their new study, published in npj Precision Oncology.
Read moreRogue’ DNA rings reveal earliest clues to deadly brain cancer’s growth
8th September 2025
An international team of scientists has revealed how rogue rings of DNA that float outside of our chromosomes – known as extrachromosomal DNA, or ecDNA – can drive the growth of a large proportion of glioblastomas, the most common and aggressive adult brain cancer. The discovery could open the door to much-needed new approaches to diagnose glioblastoma early, track its progress and treat it more effectively.
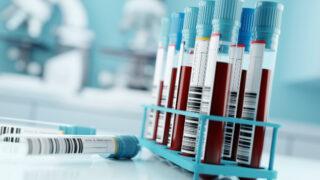
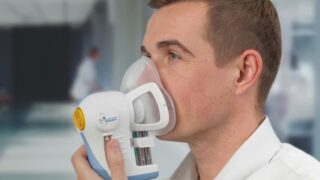
Read moreCould a breath test detect blood cancer?
23rd July 2025
Molecules exhaled in the breath may provide clues to detect blood cancer, according to new research by scientists at Barts Cancer Institute. The findings could enable the development of a blood cancer breathalyser, providing a rapid, low-cost way to detect disease.
Read more